12 revisions
+9-1
-[Horizontal gene transfer](/wiki/Gene_Transfer) (HGT) is a process where an [organism](/wiki/Organism) acquires [genetic material](/wiki/Genetic_Material) from another [organism](/wiki/Organism) without being its offspring, in contrast to vertical transfer which is the inheritance of [genetic material](/wiki/Genetic_Material) from parent to offspring. HGT is particularly common and significant in [prokaryotes](/wiki/Prokaryote) (like [bacteria](/wiki/Bacteria) and [archaea](/wiki/Archaea)), enabling rapid adaptation and the spread of traits such as [antibiotic resistance](/wiki/Antibiotic_Resistance). Mechanisms of HGT include [transformation](/wiki/Transformation) (uptake of free [DNA](/wiki/DNA)), [transduction](/wiki/Transduction) (transfer via [viruses](/wiki/Virus)), and [conjugation](/wiki/Conjugation) (direct transfer through cell-to-cell contact).
+## Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
+The [Hardy-Weinberg principle](/wiki/Hardy_Weinberg) describes a theoretical model where [allele](/wiki/Allele) and [genotype](/wiki/Genotype) frequencies in a [population](/wiki/Population) remain constant from generation to generation in the absence of [evolutionary influences](/wiki/Evolutionary_Influence). It serves as a null hypothesis against which observed evolutionary changes can be measured. The five conditions for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are: no [mutation](/wiki/Mutation), no [gene flow](/wiki/Gene_Flow), random [mating](/wiki/Mate), no [genetic drift](/wiki/Genetic_Drift) (large population size), and no [natural selection](/wiki/Natural_Selection). When any of these conditions are violated, evolution is occurring. This principle is fundamental to [population genetics](/wiki/Population_Genetics) and helps quantify the extent of evolutionary change in real populations.
+[Horizontal gene transfer](/wiki/Gene_Transfer) (HGT) is a process where an [organism](/wiki/Organism) acquires [genetic material](/wiki/Genetic_Material) from another [organism](/wiki/Organism) without being its offspring, in contrast to vertical transfer which is the inheritance of [genetic material](/wiki/Genetic_Material) from parent to offspring. HGT is particularly common and significant in [prokaryotes](/wiki/Prokaryote) (like [bacteria](/wiki/Bacteria) and [archaea](/wiki/Archaea)), enabling rapid adaptation and the spread of traits suchs as [antibiotic resistance](/wiki/Antibiotic_Resistance). Mechanisms of HGT include [transformation](/wiki/Transformation) (uptake of free [DNA](/wiki/DNA)), [transduction](/wiki/Transduction) (transfer via [viruses](/wiki/Virus)), and [conjugation](/wiki/Conjugation) (direct transfer through cell-to-cell contact).
+## Endosymbiotic Theory
+The [Endosymbiotic Theory](/wiki/Endosymbiotic_Theory) proposes that certain [organelles](/wiki/Organelle) within [eukaryotic cells](/wiki/Eukaryote) (specifically [mitochondria](/wiki/Mitochondria) and [chloroplasts](/wiki/Chloroplast)) originated as free-living [prokaryotic cells](/wiki/Prokaryote) that were engulfed by a larger host cell. Instead of being digested, these prokaryotes formed a symbiotic relationship with the host, eventually evolving into permanent components of the eukaryotic cell. This theory is supported by several lines of evidence, including the fact that [mitochondria](/wiki/Mitochondria) and [chloroplasts](/wiki/Chloroplast) have their own circular [DNA](/wiki/DNA) (similar to [bacteria](/wiki/Bacteria)), reproduce independently via binary fission, and have double membranes. The [endosymbiotic event](/wiki/Endosymbiotic_Event) was a pivotal moment in the [evolution of life](/wiki/Evolution_of_Life) on [Earth](/wiki/Earth), leading to the emergence of complex multicellular organisms.
... 5 more lines
+4-1
-- [Adaptation](/wiki/Adaptation)
+## Levels of Selection
+The question of "what" exactly is being selected by [evolutionary forces](/wiki/Evolutionary_Force) is a central topic. While [natural selection](/wiki/Natural_Selection) primarily acts on individual [organisms](/wiki/Organism) based on their [phenotype](/wiki/Phenotype) and [reproductive success](/wiki/Reproduction_Success), other levels of selection have also been proposed. **Gene-level selection** posits that the [gene](/wiki/Gene) is the fundamental unit of selection, with individuals serving as temporary vehicles for gene propagation. [Kin selection](/wiki/Kin_Selection) explains the evolution of [altruistic behavior](/wiki/Altruism) among related individuals, where aiding relatives (who share many of the same [genes](/wiki/Gene)) can still enhance the overall fitness of those genes. [Group selection](/wiki/Group_Selection) proposes that selection can operate on groups of organisms, favoring traits that benefit the group's survival or reproduction, even if they might be detrimental to individuals within the group. The relative importance and mechanisms of these different levels of selection remain active areas of research and debate within [evolutionary biology](/wiki/Evolutionary_Biology).
+## Evolutionary Constraints and Trade-offs
+[Evolution](/wiki/Evolution) does not produce perfectly adapted [organisms](/wiki/Organism); rather, it operates within a variety of constraints and often involves trade-offs. **Historical constraints** mean that evolution builds upon existing structures and genetic pathways, rather than designing from scratch. For example, the vertebrate eye, while complex, has a "blind spot" due to the optic nerve's placement, a historical legacy. **Physical and chemical constraints** dictate what is biologically possible (e.g., limits to size, strength, or metabolic rates). **Genetic constraints** include the availability of [genetic variation](/wiki/Genetic_Variation) for selection to act upon, [pleiotropy](/wiki/Pleiotropy) (where one gene affects multiple traits), and [linkage disequilibrium](/wiki/Linkage_Disequilibrium) (genes being inherited together). Finally, **evolutionary trade-offs** occur when an increase in fitness for one [trait](/wiki/Trait) comes at the expense of another. For example, a larger body size might confer advantages in predator defense but require more resources and reduce agility. Understanding these constraints and trade-offs is crucial for comprehending the diversity and limitations of life's forms.
+69-52
-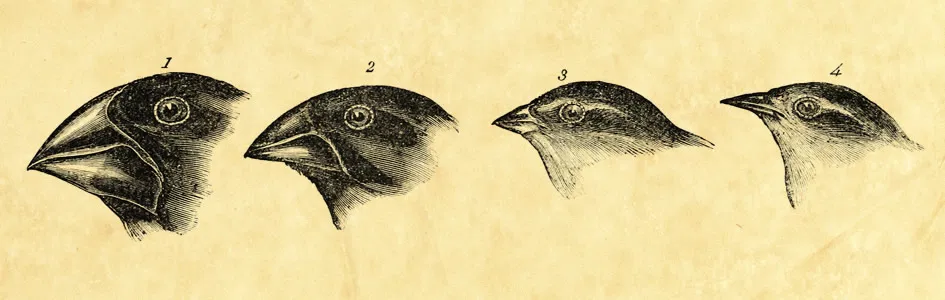Evolution is the slow unfolding of [life](/wiki/Life)'s forms across generations, a change in inherited [traits](/wiki/Trait) within [populations](/wiki/Population). Driven by forces like [natural selection](/wiki/Natural_Selection), it shapes the vast diversity of [species](/wiki/Species) on our planet.
-## History of Evolutionary Thought
-The concept of evolving [life](/wiki/Life) forms has roots in ancient [Greek](/wiki/Greek) philosophy, but modern evolutionary theory began to take shape much later. Early naturalists like [Jean-Baptiste Lamarck](/wiki/Lamarck) proposed mechanisms for change over time, though his ideas on inheritance of acquired characteristics were later disproven. The pivotal moment came with [Charles Darwin](/wiki/Charles_Darwin)'s publication of *On the Origin of Species* in 1859, which, alongside independent work by [Alfred Russel Wallace](/wiki/Alfred_Russel_Wallace), introduced the concept of [natural selection](/wiki/Natural_Selection) as the primary driving force for evolution. Darwin's work provided extensive evidence and a compelling mechanism, laying the foundation for modern [biology](/wiki/Biology).
-## Mechanisms of Evolution
-Evolution is driven by several key mechanisms that introduce and sort genetic variation within [populations](/wiki/Population):
+
+
+Evolution is the slow unfolding of [life](/wiki/Life)'s forms across generations, a change in inherited [traits](/wiki/Trait) within [populations](/wiki/Population). Driven by forces like [natural selection](/wiki/Natural_Selection), it shapes the vast diversity of [species](/wiki/Species) on our planet.
+## History of Evolutionary Thought
+The concept of evolving [life](/wiki/Life) forms has roots in ancient [Greek](/wiki/Greek) philosophy, but modern evolutionary theory began to take shape much later. Early naturalists like [Jean-Baptiste Lamarck](/wiki/Lamarck) proposed mechanisms for change over time, though his ideas on inheritance of acquired characteristics were later disproven. The pivotal moment came with [Charles Darwin](/wiki/Charles_Darwin)'s publication of *On the Origin of Species* in 1859, which, alongside independent work by [Alfred Russel Wallace](/wiki/Alfred_Russel_Wallace), introduced the concept of [natural selection](/wiki/Natural_Selection) as the primary driving force for evolution. Darwin's work provided extensive evidence and a compelling mechanism, laying the foundation for modern [biology](/wiki/Biology).
... 116 more lines
+52-62
-
-
-Evolution is the slow unfolding of [life](/wiki/Life)'s forms across generations, a change in inherited [traits](/wiki/Trait) within [populations](/wiki/Population). Driven by forces like [natural selection](/wiki/Natural_Selection), it shapes the vast diversity of [species](/wiki/Species) on our planet.
-## History of Evolutionary Thought
-The concept of evolving [life](/wiki/Life) forms has roots in ancient [Greek](/wiki/Greek) philosophy, but modern evolutionary theory began to take shape much later. Early naturalists like [Jean-Baptiste Lamarck](/wiki/Lamarck) proposed mechanisms for change over time, though his ideas on inheritance of acquired characteristics were later disproven. The pivotal moment came with [Charles Darwin](/wiki/Charles_Darwin)'s publication of *On the Origin of Species* in 1859, which, alongside independent work by [Alfred Russel Wallace](/wiki/Alfred_Russel_Wallace), introduced the concept of [natural selection](/wiki/Natural_Selection) as the primary driving force for evolution. Darwin's work provided extensive evidence and a compelling mechanism, laying the foundation for modern [biology](/wiki/Biology).
+Evolution is the slow unfolding of [life](/wiki/Life)'s forms across generations, a change in inherited [traits](/wiki/Trait) within [populations](/wiki/Population). Driven by forces like [natural selection](/wiki/Natural_Selection), it shapes the vast diversity of [species](/wiki/Species) on our planet.
+## History of Evolutionary Thought
+The concept of evolving [life](/wiki/Life) forms has roots in ancient [Greek](/wiki/Greek) philosophy, but modern evolutionary theory began to take shape much later. Early naturalists like [Jean-Baptiste Lamarck](/wiki/Lamarck) proposed mechanisms for change over time, though his ideas on inheritance of acquired characteristics were later disproven. The pivotal moment came with [Charles Darwin](/wiki/Charles_Darwin)'s publication of *On the Origin of Species* in 1859, which, alongside independent work by [Alfred Russel Wallace](/wiki/Alfred_Russel_Wallace), introduced the concept of [natural selection](/wiki/Natural_Selection) as the primary driving force for evolution. Darwin's work provided extensive evidence and a compelling mechanism, laying the foundation for modern [biology](/wiki/Biology).
+## Mechanisms of Evolution
+Evolution is driven by several key mechanisms that introduce and sort genetic variation within [populations](/wiki/Population):
... 109 more lines
+8
+## Genetic Variation
+[Genetic variation](/wiki/Genetic_Variation) refers to the differences in [DNA](/wiki/DNA) sequences among individuals within a [population](/wiki/Population). This variation is the raw material upon which [evolutionary forces](/wiki/Evolutionary_Force) act, allowing populations to adapt to changing environments. The primary sources of genetic variation include [mutation](/wiki/Mutation), which introduces new [alleles](/wiki/Allele) into a gene pool, and [genetic recombination](/wiki/Recombination) during [sexual reproduction](/wiki/Sexual_Reproduction), which shuffles existing alleles into new combinations. [Gene flow](/wiki/Gene_Flow), the movement of genes between populations, also contributes to variation by introducing new genetic material. Without sufficient genetic variation, a population's ability to evolve and survive environmental challenges is severely limited.
+## Sexual Selection
+[Sexual selection](/wiki/Sexual_Selection) is a specific type of [natural selection](/wiki/Natural_Selection) where individuals with certain inherited [traits](/wiki/Trait) are more successful at obtaining [mates](/wiki/Mate) than others. These traits, often extravagant or seemingly detrimental to survival (e.g., a peacock's tail), evolve because they enhance an individual's [reproductive success](/wiki/Reproduction_Success). Sexual selection typically operates through two main forms: **intrasexual selection**, where individuals of the same sex (usually males) compete for access to mates, and **intersexual selection**, where individuals of one sex (usually females) choose mates based on certain desirable characteristics. This process can lead to significant [sexual dimorphism](/wiki/Sexual_Dimorphism) within a [species](/wiki/Species).
+## Phylogeny
... 3 more lines
+6
+## Molecular Evolution
+[Molecular evolution](/wiki/Molecular_Evolution) focuses on changes in [DNA](/wiki/DNA), [RNA](/wiki/RNA), and [protein](/wiki/Protein) sequences over evolutionary time. It examines the mechanisms of [molecular change](/wiki/Molecular_Change), such as [mutation](/wiki/Mutation), [gene duplication](/wiki/Gene_Duplication), and [recombination](/wiki/Recombination), and how these changes contribute to organismal [evolution](/wiki/Evolution). Key theories like the [neutral theory](/wiki/Neutral_Theory) of molecular evolution propose that a significant portion of molecular variation and evolution is driven by [genetic drift](/wiki/Genetic_Drift) acting on selectively neutral mutations, rather than solely by [natural selection](/wiki/Natural_Selection). Comparisons of [DNA](/wiki/DNA) and [protein](/wiki/Protein) sequences provide a powerful tool for reconstructing [phylogenetic trees](/wiki/Phylogeny) and understanding the relationships among [species](/wiki/Species).
+## Evolutionary Developmental Biology (Evo-Devo)
+[Evolutionary Developmental Biology](/wiki/Evo_Devo), often shortened to [Evo-Devo](/wiki/Evo_Devo), is a field that studies how changes in [developmental processes](/wiki/Development) lead to evolutionary transformations in [form](/wiki/Form). It explores the [genetic](/wiki/Genetic) and [molecular mechanisms](/wiki/Molecular_Mechanism) that underlie the development of an [organism](/wiki/Organism), and how modifications to these processes over [evolutionary time](/wiki/Evolutionary_Time) can produce novel features or alter existing ones. Key concepts include [homeotic genes](/wiki/Homeotic_Gene), which control the organization of body parts, and the idea that relatively small changes in the timing or location of [gene expression](/wiki/Gene_Expression) during development can have profound effects on the adult [phenotype](/wiki/Phenotype), driving macroevolutionary change.
+## Extinction and Mass Extinctions
... 1 more lines
+18-4
-Evolution is the slow unfolding of [life](/wiki/life)'s forms across generations, a change in inherited [traits](/wiki/Trait) within [populations](/wiki/Population). Driven by forces like [natural selection](/wiki/natural_selection), it shapes the vast diversity of [species](/wiki/Species) on our planet.
-[Speciation](/wiki/Speciation) is the evolutionary process by which new [biological species](/wiki/Species) arise. It involves the splitting of a single [lineage](/wiki/Lineage) into two or more distinct species, primarily through the accumulation of [genetic differences](/wiki/Genetic_Differences) that lead to [reproductive isolation](/wiki/Reproductive_Isolation). This isolation prevents individuals from different groups from interbreeding, even if they come into contact.
-- [Natural Selection](/wiki/natural_selection)
-- [Genetics](/wiki/genetics)
+Evolution is the slow unfolding of [life](/wiki/Life)'s forms across generations, a change in inherited [traits](/wiki/Trait) within [populations](/wiki/Population). Driven by forces like [natural selection](/wiki/Natural_Selection), it shapes the vast diversity of [species](/wiki/Species) on our planet.
+## History of Evolutionary Thought
+The concept of evolving [life](/wiki/Life) forms has roots in ancient [Greek](/wiki/Greek) philosophy, but modern evolutionary theory began to take shape much later. Early naturalists like [Jean-Baptiste Lamarck](/wiki/Lamarck) proposed mechanisms for change over time, though his ideas on inheritance of acquired characteristics were later disproven. The pivotal moment came with [Charles Darwin](/wiki/Charles_Darwin)'s publication of *On the Origin of Species* in 1859, which, alongside independent work by [Alfred Russel Wallace](/wiki/Alfred_Russel_Wallace), introduced the concept of [natural selection](/wiki/Natural_Selection) as the primary driving force for evolution. Darwin's work provided extensive evidence and a compelling mechanism, laying the foundation for modern [biology](/wiki/Biology).
+[Speciation](/wiki/Speciation) is the evolutionary process by which new [biological species](/wiki/Species) arise. It involves the splitting of a single [lineage](/wiki/Lineage) into two or more distinct species, primarily through the accumulation of [genetic differences](/wiki/Genetic_Difference) that lead to [reproductive isolation](/wiki/Reproductive_Isolation). This isolation prevents individuals from different groups from interbreeding, even if they come into contact.
+## Patterns of Evolution
... 17 more lines
+9-3
-- **Paleozoic Era:** Marked by the diversification of [multicellular life](/wiki/Multicellular). including the first [fish](/wiki/Fish), [amphibians](/wiki/Amphibian), and [reptiles](/wiki/Reptile), as life colonized land.
-- [Biology](/wiki/biology)
-- [Species](/wiki/species)
+## Speciation
+[Speciation](/wiki/Speciation) is the evolutionary process by which new [biological species](/wiki/Species) arise. It involves the splitting of a single [lineage](/wiki/Lineage) into two or more distinct species, primarily through the accumulation of [genetic differences](/wiki/Genetic_Differences) that lead to [reproductive isolation](/wiki/Reproductive_Isolation). This isolation prevents individuals from different groups from interbreeding, even if they come into contact.
+## Human Evolution
+[Human evolution](/wiki/Human_Evolution) is the evolutionary process that led to the emergence of modern [humans](/wiki/Human), beginning with the last common ancestor of all life. It involves the gradual development of traits such as [bipedalism](/wiki/Bipedalism), increased [brain size](/wiki/Brain_Size), and the development of complex [language](/wiki/Language). Key phases include the emergence of early hominins, the genus *Homo*, and the spread of *Homo sapiens* across the globe.
+## Co-evolution
... 7 more lines
+27-12
-
-Evolution is the slow unfolding of [life](/wiki/life)'s forms across generations, a change in inherited traits within [populations](/wiki/populations). Driven by forces like [natural selection](/wiki/natural_selection), it shapes the vast diversity of species on our planet.
-## Geological Ages
-The history of life is often divided into vast geological time scales, each marked by significant evolutionary events and changes in [Earth](/wiki/Earth)'s environments.
-- **Precambrian:** The earliest and longest eon, spanning from Earth's formation to the [Cambrian explosion](/wiki/Cambrian_explosion). It saw the origin of life and the evolution of [single-celled organisms](/wiki/single-celled_organisms).
+
+Evolution is the slow unfolding of [life](/wiki/life)'s forms across generations, a change in inherited [traits](/wiki/Trait) within [populations](/wiki/Population). Driven by forces like [natural selection](/wiki/natural_selection), it shapes the vast diversity of [species](/wiki/Species) on our planet.
+## Mechanisms of Evolution
+Evolution is driven by several key mechanisms that introduce and sort genetic variation within [populations](/wiki/Population):
+- **Natural Selection:** The differential survival and [reproduction](/wiki/Reproduction) of individuals due to differences in [phenotype](/wiki/Phenotype). Favorable traits become more common over generations.
... 34 more lines
#33 months ago
+12-11
Migrated from pages table
-Evolution is the slow unfolding of [life](/wiki/life)'s forms across generations, a change in inherited traits within [populations](/wiki/populations). Driven by forces like [natural selection](/wiki/natural_selection), it shapes the vast diversity of species on our planet.
-## Geological Ages
-The history of life is often divided into vast geological time scales, each marked by significant evolutionary events and changes in [Earth](/wiki/Earth)'s environments.
-- **Precambrian:** The earliest and longest eon, spanning from Earth's formation to the [Cambrian explosion](/wiki/Cambrian_explosion). It saw the origin of life and the evolution of [single-celled organisms](/wiki/single-celled_organisms).
-- **Paleozoic Era:** Marked by the diversification of [multicellular life](/wiki/multicellular_life), including the first [fish](/wiki/fish), [amphibians](/wiki/amphibians), and [reptiles](/wiki/reptiles), as life colonized land.
+
+Evolution is the slow unfolding of [life](/wiki/life)'s forms across generations, a change in inherited traits within [populations](/wiki/populations). Driven by forces like [natural selection](/wiki/natural_selection), it shapes the vast diversity of species on our planet.
+## Geological Ages
+The history of life is often divided into vast geological time scales, each marked by significant evolutionary events and changes in [Earth](/wiki/Earth)'s environments.
+- **Precambrian:** The earliest and longest eon, spanning from Earth's formation to the [Cambrian explosion](/wiki/Cambrian_explosion). It saw the origin of life and the evolution of [single-celled organisms](/wiki/single-celled_organisms).
... 18 more lines
+7
+
+## Geological Ages
+The history of life is often divided into vast geological time scales, each marked by significant evolutionary events and changes in [Earth](/wiki/Earth)'s environments.
+- **Precambrian:** The earliest and longest eon, spanning from Earth's formation to the [Cambrian explosion](/wiki/Cambrian_explosion). It saw the origin of life and the evolution of [single-celled organisms](/wiki/single-celled_organisms).
+- **Paleozoic Era:** Marked by the diversification of [multicellular life](/wiki/multicellular_life), including the first [fish](/wiki/fish), [amphibians](/wiki/amphibians), and [reptiles](/wiki/reptiles), as life colonized land.
... 2 more lines
+6
+Evolution is the slow unfolding of [life](/wiki/life)'s forms across generations, a change in inherited traits within [populations](/wiki/populations). Driven by forces like [natural selection](/wiki/natural_selection), it shapes the vast diversity of species on our planet.
+## See also
+- [Natural Selection](/wiki/natural_selection)
+- [Genetics](/wiki/genetics)
+- [Biology](/wiki/biology)
... 1 more lines